The xcore-200 Multi-Channel Audio Board¶
An application of the USB audio framework is provided specifically for the XK_AUDIO_216_MC_AB
hardware described in USB Audio hardware platforms and is implemented on an xcore-200
series dual tile device. The related code can be found in app_usb_aud_xk_216_mc.
The design supports upto 8 channels of analogue audio input/output at sample-rates up to 192kHz
(assuming the use of I²S). This can be further increased by utilising TDM. It also supports S/PDIF,
ADAT and MIDI input and output as well as the mixing functionalty of lib_xua.
The design uses the following tasks:
XMOS USB Device Driver (XUD)
Endpoint 0
Endpoint Buffer
Decoupler
AudioHub Driver
Mixer
S/PDIF Transmitter
S/PDIF Receiver
ADAT Receiver
Clockgen
MIDI
The software layout of the USB Audio 2.0 Reference Design running on the xcore.ai device is shown in Fig. 2.
Each circle depicts a task running in a single core concurrently with the other tasks. The lines show the communication between each task.
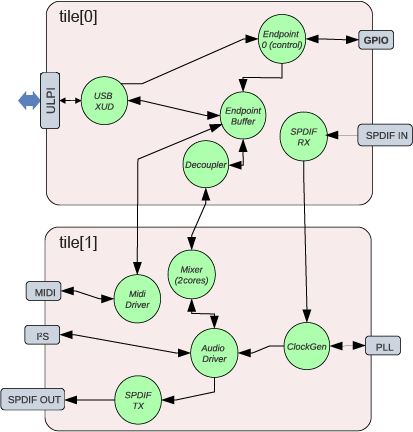
Fig. 2 xcore-200 Multichannel Audio system/task diagram¶
The app_usb_aud_xk_216_mc application uses the functions provided in lib_board_support
for master clock generation and audio hardware configuration.
The functions xk_audio_216_mc_ab_AudioHwInit() and
xk_audio_216_mc_ab_AudioHwConfig() are called at various points during initialisation and
runtime to initialise and configure the audio hardware.
For further details on the hardware platform and the functions available for configuring it refer to lib_board_support documentation.
Audio hardware¶
Clocking and Clock Selection¶
The board includes two options for master clock generation:
A single oscillator with a Phaselink PLL to generate fixed 24.576MHz and 22.5792MHz master-clocks.
A Cirrus Logic CS2100 clock multiplier allowing the master clock to be generated from a xcore derived reference clock.
The master clock source is controlled by a mux which, in turn, is controlled by bit 5 of PORT 8C:
Value |
Source |
|---|---|
0 |
Master clock is sourced from PhaseLink PLL |
1 |
Master clock is source from Cirrus Clock Multiplier |
The clock-select from the phaselink part is controlled via bit 7 of PORT 8C:
Value |
Frequency |
|---|---|
0 |
24.576MHz |
1 |
22.579MHz |
DAC and ADC¶
The board is equipped with a single multi-channel audio DAC (Cirrus Logic CS4384) and a single multi-channel ADC (Cirrus Logic CS5368) giving 8 channels of analogue output and 8 channels of analogue input. Configuration of both the DAC and the ADC takes place over I²C.
Configuring audio hardware¶
All of the external audio hardware is configured using lib_board_support.
Note
lib_board_support has the I²C library (lib_i2c) in its dependency list.
The hardware targeted is the XMOS XU216 Multichannel Audio board (XK-AUDIO-216-MC).
The functions xk_audio_216_mc_ab_AudioHwInit() and
xk_audio_216_mc_ab_AudioHwConfig() are called at various points during initialisation and
runtime to initialise and configure the audio hardware.
The audio hardware configuration is set in the config structure of type
xk_audio_216_mc_ab_config_t which is passed to the
xk_audio_216_mc_ab_AudioHwInit() and xk_audio_216_mc_ab_AudioHwConfig() functions.
static const xk_audio_216_mc_ab_config_t config = {
// clk_mode
CLK_MODE,
// codec_is_clk_master
CODEC_MASTER,
// usb_sel
(USB_SEL_A ? AUD_216_USB_A : AUD_216_USB_B),
// pcm_format
XUA_PCM_FORMAT,
// pll_sync_freq
PLL_SYNC_FREQ
};
The AudioHwInit() function is implemented to make a call to the lib_board_support
function xk_audio_216_mc_ab_AudioHwInit() to power up and initialise the audio hardware
ready for a configuration.
The AudioHwConfig() function configures the audio hardware post initialisation.
It is called each time a sample rate or stream format change occurs.
It is implemented to make a call to the lib_board_support function
xk_audio_216_mc_ab_AudioHwConfig().
For further details on the hardware platform and the functions available for configuring it refer to lib_board_support documentation.
Validated build options¶
The reference design can be built in several ways by changing the build options. These are described in Configuration defines.
The design has only been fully validated against the build options as set in the application as distributed in the CMakeLists.txt. See Build configurations for details and general information on build configuation naming scheme.
These fully validated build configurations are enumerated in the supplied CMakeLists.txt.
In practise, due to the similarities between the xcore-200 and xcore.ai series feature set, it is fully expected that all listed xcore-200 series configurations will operate as expected on the xcore.ai series and vice versa.
The build configuration naming scheme employed in the CMakeLists.txt is shown in Table 11.
Feature |
Option 1 |
Option 2 |
|---|---|---|
Audio Class |
1 |
2 |
USB Sync Mode |
async: A |
sync: S |
I²S Role |
slave: S |
master: M |
Input |
enabled: i (channel count) |
disabled: x |
Output |
enabled: i (channel count) |
disabled: x |
MIDI |
enabled: m |
disabled: x |
S/PDIF input |
enabled: s |
disabled: x |
S/PDIF input |
enabled: s |
disabled: x |
ADAT input |
enabled: a |
disabled: x |
ADAT output |
enabled: a |
disabled: x |
DSD output |
enabled: d |
disabled: x |
e.g. A build configuration named 2AMi10o10xsxxxx would signify: Audio class 2.0 running in asynchronous mode. The xcore is I²S master. Input and output enabled (10 channels each), no MIDI, S/PDIF input, no S/PDIF output, no ADAT or DSD.
In addition to this some terms may be appended onto a build configuration name to signify additional options. For example, tdm may be appended to the build configuration name to indicate the I²S mode employed.